School streets implementation: A machine learning perspective 145
References
880 Cities. School Streets Guidebook. City of Victoria, Capital Regional
District of British Columbia, 2019.
Brand, Lasse, Susanne Böhler, and Siegfried Rupprecht. Topic Guide:
Sustainable Urban Mobility Planning in Smaller Cities and Towns.
Rupprecht Consult, 2021.
Bridges, Christina N., Tyler M. Prochnow, Emily C. Wilkins, Ke shia
M. Pollack Porter, and M. Renée Umstattd Meyer. “Examin-
ing the Implementation of Play Streets: A Systematic Review of
the Grey Literature.” Journal of Public Health Management and
Practice 26, no. 3 (2020): E1–E10. https://doi.org/10.1097/PHH.
0000000000001015.
City of Edinburgh Council. “Streets Ahead, Road Safety in Edinburgh.
School Streets.” Accessed April 10, 2020, at https://www.streetsa-
headedinburgh.org.uk/school-streets-1/school-streets.
City of Victoria. “School Streets. The School Streets program creates
safer school zones and encourages active transportation.” City of
Vic toria. 2022. Accessed April 10, 2022, at https://www.victoria. ca/ -
EN/main/residents/streets-transportation/walk-roll-transit/school-
programs/school-streets.html.
Clarivate. Web of Science. n.d. Accessed April 10, 2024, at https://www.
webofscience.com/wos/woscc/summary/6d7384cd-379f-477d-
9581-eb2df65998e9-e194a1f6/relevance/1.
Clarke, Richard. School streets: Putting children and the planet rst.
Child Health Initiative’s Advocacy Hub, FIA Foundation, 2022.
Davis, Adrian. School Street Closures and Trac Displacement Project:
A Literature Review with semi-structured interviews. Transport Re-
search Institute, Edinburgh Napier University, 2020.
Goodfellow, Ian J., Jean Pouget-Abadie, Mehdi Mirza, et al. “Genera-
tive Adversarial Nets.” In Advances in Neural Information Process-
ing Systems (NIPS), edited by Zoubin Ghahramani, Max Welling,
Corinna Cortes, Neil D. Lawrence and Kilian Q. Weinberger. Curran
Associates, 2014.
Grabowska, Marta, and Anna Szmigiel-Franz. Szkolna ulica: Raport
z pilotażu. Biuro Zrównoważonej Mobilności Urzędu Miejskiego
Wrocławia, 2020.
Isola, Phillip, Jun-Yan Zhu, Tinghui Zhou, and Alexei A. Efros. “Image-to-
-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks.” In IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR),
2017, 5967–5976.
Keaney, David, and Paul Tovey. School Streets Pilot Project – Six Month
Update and Review. Report, Solihull Metropolitan Borough Coun-
cil, 2018.
Lawrence, Paul, and Steven Murrell. School Streets Pilot Project Eva
luation. Transport and Environment Committee, The City of Edin-
burgh Council, 2016.
Linton, Tyler, Doolin O’Reilly, Dominique Humbert, and Caroline Bur-
well. School Streets Timed Trac Restrictions Toolkig for Profes-
sionals. Hackney School Streets, 2021.
LPW. “Droga na szóstkę: Ocena bezpieczeństwa ruchu drogowego wo-
kół wybranych szkół podstawowych: Raport końcowy, Szkoła pod-
stawowa nr 41; 157; 175; 195; 323; 327.” Zarząd Dróg Miejskich,
Urząd m.st. Warszawy, 2020.
Mapbox. “Mapbox Studio.” Generated September 2023. Accessed Feb-
ruary 2, 2024, at https://www.mapbox.com/about/maps.
My Journey: Helping Hampshire Get Around. “Southampton School
Streets programme.” Southampton City Council. 2021. Accessed
April 10, 2022, at https://myjourneyhampshire.com/education/
school-streets/southampton-school-streets-programme/.
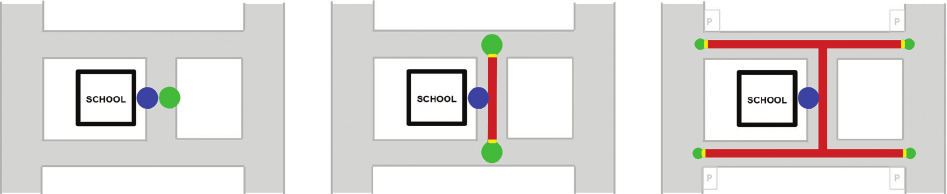
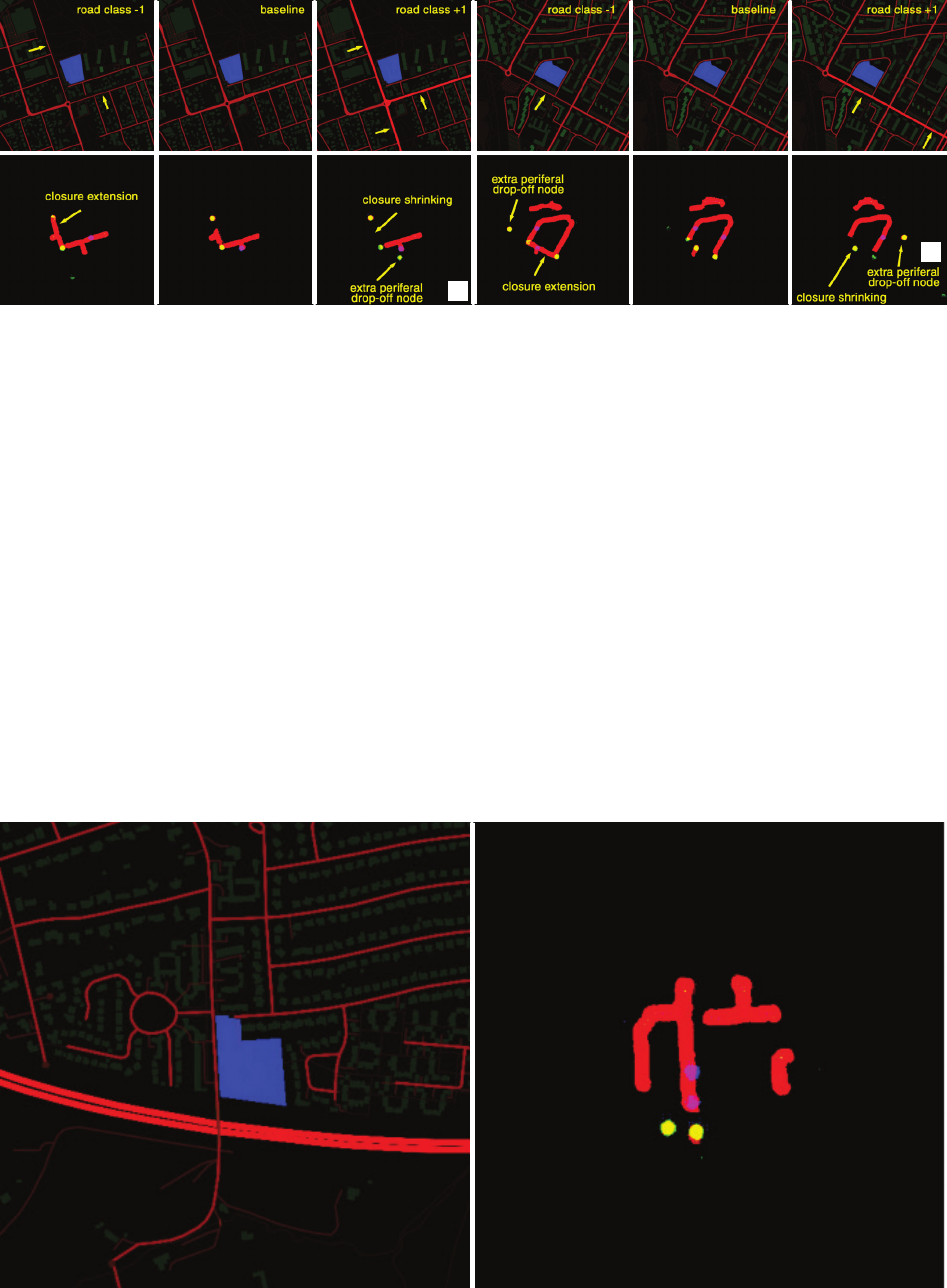
To some extent the failure in this case could be partial-
ly justied by the negative assessment of viability of the
Bonaly Primary School for the implementation of a school
street closure program (Lawrence, Murrell 2016). Due to
the limited training sample, the algorithm was trained to
always generate a closure zone, even if the contexts are not
favourable. This hard requirement sometimes leads to in-
correct proposals. As the tool was being developed, a large
number of school street programs were implemented as
a result of the COVID-19 pandemic (Clarke 2022). Cur-
rently, a much larger dataset of successful closures can be
compiled to train the next iteration of the algorithm. Anoth-
er large problem arises from the incompleteness of the ana-
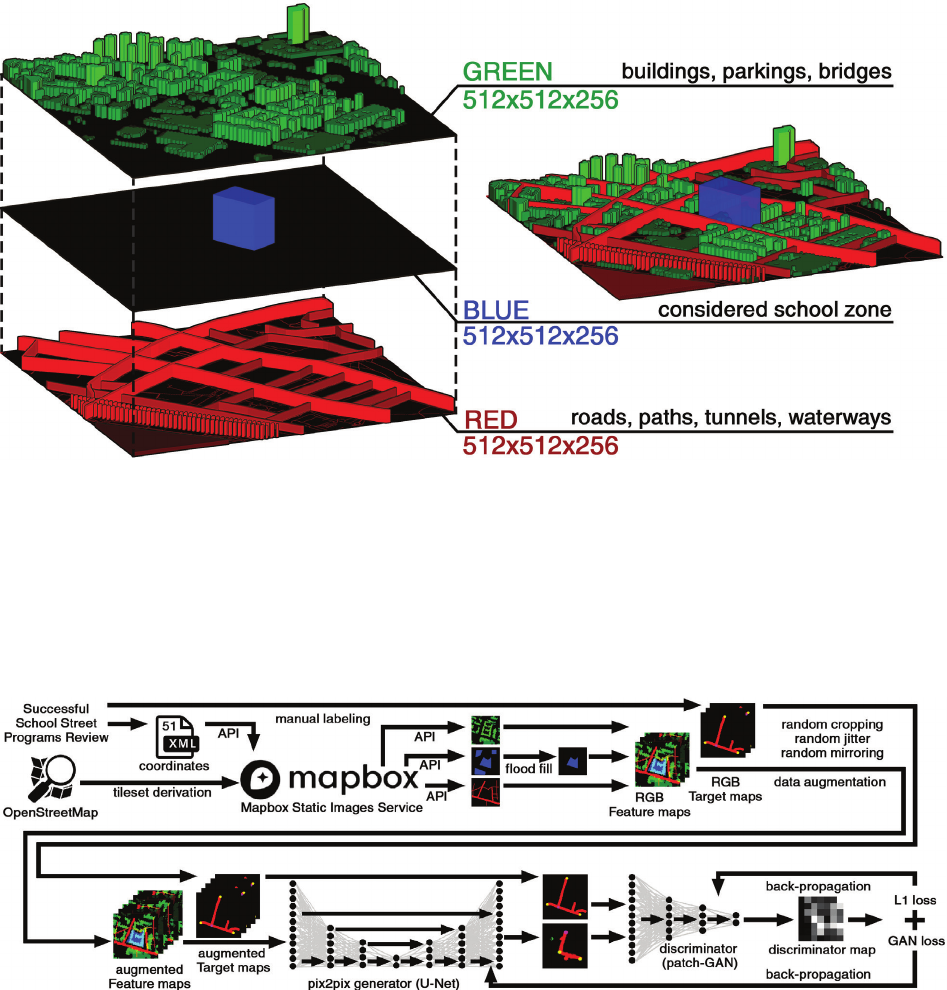
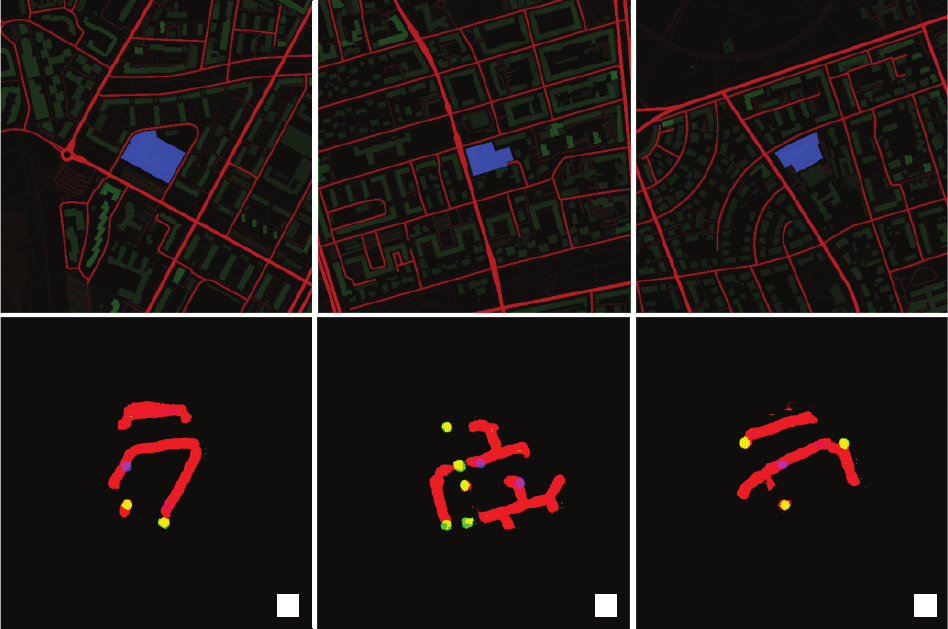
lysed contexts and the low resolution of the accessible data.
The utilized feature maps do not fully reect the real-world
complexities of implementing school street closures. While
the tool could denitely benet from more extensive, high-
resolution data, such data is not readily available or ma-
chine-friendly. These extended contexts could include:
– trac analysis, such as the road safety audit, recorded
incidents aecting the school community and trac inten-
sity measurements,
–
communication habits of the students and their parents,
– functional audit,
– database of stakeholders aected by the closure and
their characteristics,
– air quality and pollution measurements,
– records of other programs related to school street clo-
sures at the candidate school, including physical activity
encouragement projects, play streets, school gardening ini-
tiatives, local community activization, etc.
A more comprehensive data collection and integration
could improve the tool’s eectiveness and would proba-
bly increase the capabilities of the system. However, an
increase in the number of compiled context sources would
also reduce the applicability of the algorithm only to the
areas, which have these contexts recorded and accessible.
The current version of the algorithm can be applied to any
school that is represented on OpenStreetMap. Future re-
search should focus on expanding the dataset and improv-
ing the algorithm’s adaptability to diverse urban contexts.
Additionally, a collaborative approach involving stake-
holders from various sectors, including education, trans-
portation, and public health, is crucial for the successful
implementation and scaling of school street programs. By
doing so, cities can create safer, healthier and more vibrant
urban spaces that prioritize the well-being of children and
the entire urban community.
Conclusions
In conclusion, this study demonstrates the potential of
data-driven approaches to enhance the planning and im-
plementation of school street programs. The integration of
machine learning tools can streamline the selection pro-
cess and improve the design of these interventions, making
them more eective and context-sensitive. Policymakers
and urban planners should consider investing in the de-
velopment and deployment of such tools to support their
urban mobility goals.